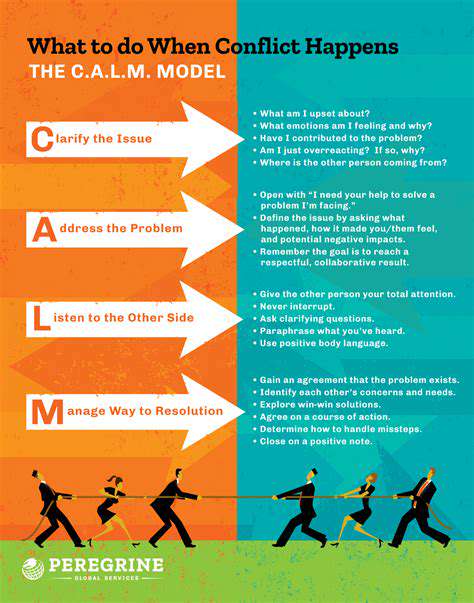
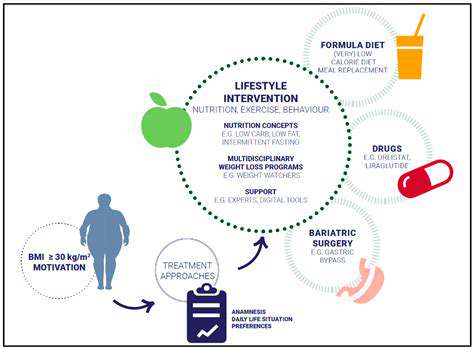
The Science of Pet Food: Digestibility and Nutrients
Carbohydrates: The Body's Primary Fuel Source
Carbohydrates are essential for providing energy to the body, particularly for the brain and muscles. They are broken down into glucose, which is used as the primary fuel source for cellular processes. Different types of carbohydrates impact digestion and energy release differently. Simple carbohydrates, like sugars, are quickly digested and absorbed, leading to a rapid increase in blood glucose levels. Complex carbohydrates, found in whole grains and vegetables, are digested more slowly, providing a sustained energy release and promoting better blood sugar regulation. Understanding the balance of carbohydrates in a pet's diet is crucial for maintaining optimal energy levels and preventing metabolic issues.
The type and amount of carbohydrates in a pet food formula directly affect its nutritional value and digestibility. High-quality pet foods utilize complex carbohydrates that provide sustained energy, supporting healthy bodily functions. Conversely, excessive simple carbohydrates can lead to spikes and crashes in blood glucose levels, potentially contributing to weight gain and other health problems. A balanced carbohydrate profile is vital for a pet's overall well-being.
Fats: Essential for Cellular Function and Structure
Fats play a crucial role in various bodily functions, including insulation, hormone production, and cell membrane structure. Essential fatty acids (EFAs), such as omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids, are crucial for maintaining healthy skin, coat, and immune function. They are vital for proper cognitive development and overall health, particularly in growing pets.
The quality and type of fats in pet food are important factors in digestibility and nutrient absorption. High-quality fats from animal sources or plant-based oils contribute to a healthy fat profile. However, excessive amounts of unhealthy fats can negatively impact a pet's health and contribute to weight problems.
Digestibility of Carbohydrates: A Crucial Consideration
The digestibility of carbohydrates is a key factor in evaluating the nutritional value of pet food. Efficient digestion ensures that the body can extract the necessary nutrients from the carbohydrates, providing sustained energy without causing digestive distress. Some carbohydrates are more readily digested than others, impacting the overall nutritional profile of the food.
Factors like the source of carbohydrates and processing methods greatly influence their digestibility. Proper digestion is essential for extracting energy and preventing digestive issues like gas, bloating, and diarrhea. In pet food formulations, the digestibility of carbohydrates is often optimized to maximize energy provision and minimize adverse effects.
Fats and Nutrient Absorption: A Synergistic Relationship
Fats play a vital role in the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins (A, D, E, and K) in the body. These vitamins are essential for various bodily functions, including immune function, vision, and bone health. Therefore, the presence of adequate amounts of healthy fats in pet food is crucial for ensuring the efficient absorption of these vital nutrients.
The Role of Fiber in Carbohydrate Metabolism
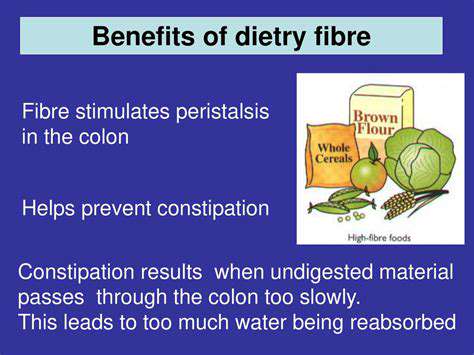
Dietary fiber, a type of complex carbohydrate, is crucial for digestive health. It promotes healthy gut bacteria, aids in regular bowel movements, and contributes to a feeling of fullness. Including fiber in pet food formulations can help manage weight and promote healthy digestion, which is essential for overall well-being. Different types of fiber have varying levels of digestibility, impacting their role in the digestive process.
Energy Balance and Weight Management: The Role of Carbohydrates and Fats
A balanced intake of carbohydrates and fats is crucial for maintaining a healthy weight in pets. Inadequate or excessive intake of either macronutrient can lead to weight problems. Understanding the energy density of different carbohydrates and fats in a pet food is essential for formulating a balanced diet that supports a healthy weight. Careful consideration of the digestibility of these macronutrients is essential for optimizing energy provision and preventing weight-related health issues.
The Impact of Processing on Carbohydrate and Fat Digestibility
Processing methods used for pet food ingredients can significantly affect the digestibility of carbohydrates and fats. Different processing techniques can alter the structure and composition of these nutrients, impacting their absorption and utilization by the body. Understanding the impact of processing on the digestibility of these key nutrients is vital for formulating pet foods that meet the specific needs of different breeds and life stages. Proper processing techniques can maximize the nutritional value and digestibility of ingredients.
Beyond the Basics: Considering Specialized Needs

Beyond the Fundamental Concepts of Speed
Understanding speed is more than just a simple calculation; it's a fundamental concept in physics that underpins many other principles. This understanding extends beyond the basic formula to encompass the nuances of acceleration, velocity, and the various factors that influence speed. Speed, in its broadest sense, is a measure of how quickly an object changes its position over time. It reflects the rate of change in distance.
Different contexts require different approaches to understanding speed. For example, calculating the speed of a car on a highway is vastly different than calculating the speed of a molecule in a gas. In each case, the context and the relevant variables must be carefully considered for an accurate assessment.
The Role of Time in Speed Calculations
Time is an integral part of any speed calculation. A change in position without considering the time it took for that change to occur is meaningless. Proper time measurement is crucial to determine the true speed of an object. Accurate timing devices are essential for precision in speed calculations, especially in dynamic environments.
We often take for granted the importance of precise time measurement in everyday situations, like checking the speed of a car. Yet, without precise timing, the calculated speed could be inaccurate, hindering our understanding of the object's motion.
Different Types of Speed
The concept of speed isn't limited to a single definition. There are different types of speed, each with its own specific meaning. Average speed, for example, is the overall speed over a period of time, while instantaneous speed is the speed at a specific moment in time. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for accurate analysis.
Another crucial distinction is between speed and velocity. While speed is a scalar quantity, describing only the rate of motion, velocity is a vector quantity, also describing the rate of motion, but also including the direction of motion.
The Impact of Acceleration on Speed
Acceleration plays a significant role in how speed changes over time. A constant acceleration will result in a continuously changing speed, whereas a lack of acceleration means a steady speed. Understanding the relationship between acceleration and speed is critical in many applications, from calculating the motion of planets to analyzing the performance of vehicles.
Factors Influencing Speed
External forces, such as friction, gravity, and air resistance, can significantly impact an object's speed. The interplay of these forces can be complex, but it's crucial to consider them when studying speed and motion. For example, air resistance will affect the speed of a falling object, while gravity influences the speed of a projectile.
Applications of Speed in Various Fields
The concept of speed is fundamental in various fields, including physics, engineering, and even sports. In physics, it is crucial to understand how speed relates to other quantities like momentum and energy. In engineering, it is used to optimize the performance of machines and structures. In sports, understanding and measuring speed can dramatically improve performance analysis and athlete training.
Measuring and Calculating Speed
Accurate measurements of speed are essential in many situations. From measuring the speed of a bullet to determining the speed of sound, precise measuring instruments are used. Furthermore, calculations involving speed require a solid understanding of the underlying principles and a careful application of formulas. Proper use of tools and techniques is critical for accurate results in any speed-related measurement or calculation.
Different methods and instruments are used, depending on the specific application, ensuring that the chosen method aligns with the desired level of accuracy and precision needed for the task at hand.
Read more about The Science of Pet Food: Digestibility and Nutrients
Hot Recommendations
- Best Pet Bowls: Stainless Steel and Ceramic
- Pet Hydration: Why It's Crucial
- Stop Counter Surfing: Training Your Dog to Stay Off
- Pet Hypothyroidism: Symptoms and Management
- Signs of Pet Liver Disease: What to Watch For
- Pet Emergency Kits: What to Pack
- Dangers of Xylitol: Toxic to Dogs
- Dealing with Pet Diarrhea: When to See a Vet
- Preparing Pets for Travel: Tips for a Smooth Trip
- Pet Depression: Recognizing the Signs