Addressing Food Sensitivities in Cats
Recognizing the Signs of Food Sensitivity in Cats

Identifying Common Food Sensitivities
Food sensitivities, encompassing a range of reactions from mild discomfort to severe allergic responses, can manifest in various ways. Understanding the common signs and symptoms is crucial for early detection and appropriate management. Recognizing these indicators empowers individuals to seek professional help and implement strategies to minimize potential harm. Many people experience gastrointestinal issues like bloating, gas, and diarrhea after consuming certain foods. These symptoms can be subtle and easily overlooked, leading to delayed diagnosis.
Beyond the digestive system, skin rashes, hives, and itching can also be indicators of a food sensitivity. These cutaneous reactions can vary in severity and location, making them sometimes difficult to pinpoint as a food-related issue. Other potential symptoms include headaches, fatigue, and even mood swings. It is important to remember that food sensitivities can affect individuals differently, and the symptoms can differ from person to person.
The Role of Diet in Managing Food Sensitivities
Adopting a suitable diet plays a pivotal role in managing food sensitivities. Identifying trigger foods and eliminating them from the diet can significantly improve symptoms. A dietary approach often involves keeping a detailed food journal to track potential reactions. This meticulous recording helps in pinpointing specific foods that evoke adverse responses.
This dietary approach often involves carefully selecting foods that are known to be less likely to cause reactions. This process may require significant lifestyle adjustments, but the benefits of reduced discomfort and improved overall well-being can make the effort worthwhile. Furthermore, a balanced diet rich in nutrients essential for overall health is crucial during this process.
The Importance of Professional Diagnosis
While recognizing potential symptoms can be a valuable first step, obtaining a proper diagnosis from a healthcare professional is crucial for effective management. A medical professional can conduct thorough assessments, including medical history reviews, physical examinations, and potentially, allergy testing. This ensures an accurate identification of the specific food or foods causing the reactions.
A professional diagnosis is essential to ensure the correct treatment plan is implemented. The accuracy of diagnosis directly impacts the efficacy of the treatment and avoidance strategies. Without a proper diagnosis, self-treatment strategies might prove ineffective and even harmful.
Understanding the Underlying Mechanisms
Food sensitivities occur due to a variety of factors, including the body's immune response to certain food proteins. The immune system's reaction can trigger a cascade of events leading to various symptoms. This complex interplay highlights the importance of understanding the underlying mechanisms to better manage these sensitivities. The exact mechanisms behind these reactions are still being researched, but the role of the immune system is central to the understanding.
Further research into the underlying mechanisms is crucial for developing more effective diagnostic and treatment strategies. This knowledge will allow for a more personalized approach to managing food sensitivities and improving patient outcomes.
Dietary Strategies for Elimination and Substitution
Implementing dietary strategies for eliminating trigger foods and substituting them with suitable alternatives is a core component of managing food sensitivities. This involves carefully reading food labels to identify potential allergens and avoiding cross-contamination during food preparation. This meticulous approach is essential to prevent accidental exposure and potential reactions.
The key is to find suitable replacements that provide the necessary nutrients and satisfy the individual's dietary preferences. This might involve exploring alternative food sources, recipes, and cooking methods to ensure nutritional adequacy. This process can be challenging but is essential for maintaining a healthy lifestyle.
Long-Term Management and Prevention
Long-term management of food sensitivities involves continuous monitoring and adjustments to the diet. Regular check-ups with a healthcare professional are vital for tracking progress and adjusting the management plan as needed. This proactive approach helps in preventing future reactions and maintaining overall well-being.
Proactive measures, like careful meal planning and meticulous food preparation, are key to successful long-term management. This approach ensures that individuals can enjoy a wide variety of foods while minimizing the risk of adverse reactions. Education and awareness play a significant role in preventing further complications.
Differentiating Between Food Allergies and Sensitivities
Understanding Food Allergies
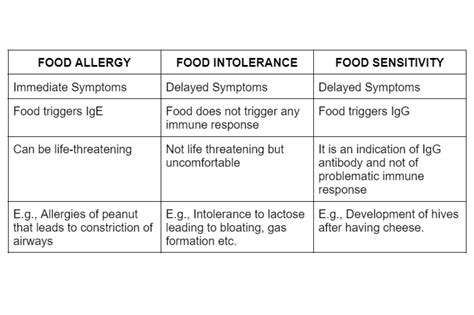
Food allergies are a serious health concern that affects millions of people worldwide. They occur when the body's immune system mistakenly identifies a harmless food protein as a threat. This triggers a chain reaction that can lead to a range of symptoms, from mild discomfort to life-threatening anaphylaxis. It's crucial to understand the difference between a food allergy and a food intolerance, as the latter doesn't involve the immune system and typically presents with less severe reactions.
Identifying the symptoms of a food allergy is vital for prompt treatment and potentially preventing serious complications. Recognizing the early signs can significantly impact the severity of the reaction. Early intervention often leads to better outcomes and can save lives.
Common Food Allergens
Many foods can trigger allergic reactions, but some are more common than others. Common culprits include peanuts, tree nuts, milk, eggs, soy, wheat, fish, and shellfish. These foods are often found in various processed foods and can easily be introduced into the diet, making them particularly significant allergens for many people.
It's important to note that exposure to even small amounts of these allergens can sometimes trigger a reaction in susceptible individuals. This underscores the need for caution and awareness when consuming foods containing these known allergens.
Symptoms of a Food Allergy
The symptoms of a food allergy can vary greatly from person to person and can range from mild to severe. Some common symptoms include hives, itching, swelling, difficulty breathing, nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. Recognizing these symptoms is critical for immediate action and preventing potential complications.
In severe cases, a food allergy can trigger a life-threatening reaction called anaphylaxis. Symptoms of anaphylaxis include a rapid drop in blood pressure, difficulty breathing, and loss of consciousness. It's crucial to seek immediate medical attention if you experience these severe symptoms.
Diagnosing Food Allergies
Diagnosing a food allergy typically involves a combination of a detailed medical history, physical examination, and allergy testing. A physician will assess the patient's symptoms and potential triggers to understand the severity and nature of the reaction.
Allergy testing, such as skin prick tests or blood tests, can help identify specific allergens that might be responsible for the reaction. These tests help confirm the suspected allergens and guide treatment strategies.
Managing Food Allergies
Managing food allergies requires careful planning and avoidance of the trigger foods. This involves meticulous reading of food labels and understanding potential cross-contamination risks in restaurants or shared food environments. Implementing strategies to avoid allergens is crucial for preventing allergic reactions and maintaining a healthy lifestyle. Careful planning also includes carrying appropriate emergency medication, like epinephrine auto-injectors, and educating others about the allergy.
Working with a healthcare professional and an allergist is important for developing a personalized management plan that addresses specific needs and concerns. This personalized approach helps in effectively mitigating the risks and challenges associated with food allergies.
Read more about Addressing Food Sensitivities in Cats
Hot Recommendations
- Best Pet Bowls: Stainless Steel and Ceramic
- Pet Hydration: Why It's Crucial
- Stop Counter Surfing: Training Your Dog to Stay Off
- Pet Hypothyroidism: Symptoms and Management
- Signs of Pet Liver Disease: What to Watch For
- Pet Emergency Kits: What to Pack
- Dangers of Xylitol: Toxic to Dogs
- Dealing with Pet Diarrhea: When to See a Vet
- Preparing Pets for Travel: Tips for a Smooth Trip
- Pet Depression: Recognizing the Signs