Nutritional Needs of Growing Puppies
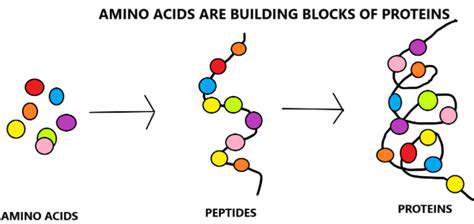
Protein: The Fundamental Component of Growth
Proteins are essential biomolecules that play a crucial role in virtually every biological process within the human body. They are composed of amino acids, linked together in specific sequences to form complex three-dimensional structures. These structures are vital for the proper functioning of cells and tissues. The diverse functions of proteins are extensive, ranging from catalyzing biochemical reactions to transporting molecules and providing structural support.
Protein Synthesis and its Importance
Protein synthesis is the process by which cells create proteins. This process, driven by genetic instructions encoded in DNA, is a complex and tightly regulated series of steps. Understanding protein synthesis is crucial to comprehending how cells function and respond to various stimuli. Errors in protein synthesis can lead to various diseases and disorders.
Essential Amino Acids and their Roles
Of the twenty amino acids required for protein synthesis, nine are considered essential, meaning the body cannot produce them on its own. These essential amino acids must be obtained through dietary intake. A balanced diet rich in protein sources like meat, poultry, fish, eggs, and legumes ensures the body receives these vital building blocks. Deficiencies in essential amino acids can hinder growth and development, impacting overall health.
Protein's Role in Muscle Growth and Repair
Proteins are fundamental for building and repairing muscles. During exercise, muscle fibers experience microscopic damage. Protein consumption provides the raw materials for repairing these damaged fibers and building new ones, ultimately leading to muscle growth and strength gains. Protein intake is especially important for athletes and individuals involved in intense physical activity. Adequate protein intake supports muscle recovery and promotes overall athletic performance.
Protein's Role in Enzyme Function
Many enzymes, which are biological catalysts, are proteins. These proteins facilitate biochemical reactions within the body, accelerating the rate of these processes. Enzymes are essential for vital functions like digestion, metabolism, and energy production. Without enzymes, these processes would occur at an extremely slow rate, making them impossible for the body to maintain.
The Impact of Protein on Hormone Production
Various hormones, responsible for regulating numerous bodily functions, are also proteins. These hormones act as chemical messengers, conveying signals throughout the body. Hormones play crucial roles in growth, development, metabolism, and reproduction. A proper protein intake is essential for the production of these vital hormones.
Protein's Influence on Immune System Function
Proteins play a significant role in the immune system's ability to fight infections and diseases. Antibodies, a type of protein, are crucial components of the immune response. Antibodies recognize and neutralize harmful pathogens, protecting the body from various illnesses. A sufficient protein intake strengthens the immune system, enhancing its ability to combat infections.
Fats: Supporting Brain Development and Energy

Essential Fatty Acids for Brain Function
Fats play a crucial role in brain development, particularly the essential fatty acids omega-3 and omega-6. These fats are vital components of brain cell membranes, impacting their structure and function. Adequate intake of these essential fats during crucial developmental stages, like infancy and childhood, is critical for optimal brain growth and cognitive abilities. The brain is highly dependent on these fatty acids for its normal functioning, especially in areas responsible for learning and memory.
Omega-3 fatty acids, specifically DHA (docosahexaenoic acid), are particularly important for brain structure and function. They are concentrated in the gray matter of the brain and contribute significantly to the development of nerve cells and connections. Studies have shown a strong correlation between omega-3 intake and improved cognitive performance in children and adolescents.
Types of Fats and Their Impact
Not all fats are created equal. While essential fatty acids are crucial, saturated and trans fats can have negative impacts on brain health. Consuming excessive amounts of saturated and trans fats can contribute to inflammation and potentially disrupt the delicate balance of brain cell function. Focusing on healthy fats, like those found in avocados and nuts, and limiting unhealthy fats is vital for optimal brain development and overall health.
Unsaturated fats, including monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats, are generally considered healthier. These fats help maintain the fluidity of cell membranes, which is essential for proper communication between brain cells. Incorporating these healthy fats into your diet can support the structural integrity and optimal functioning of the brain.
Dietary Sources of Healthy Fats
A balanced diet rich in healthy fats is essential for supporting brain development. Excellent sources of omega-3 fatty acids include fatty fish like salmon, tuna, and mackerel. These fish are packed with nutrients beneficial for brain health. Including these foods in your diet is a simple yet effective way to ensure adequate omega-3 intake.
Other excellent sources of healthy fats include avocados, nuts, seeds, and olive oil. These foods provide a variety of nutrients, including vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants, which further support brain health and overall well-being. Including a variety of these foods in your diet promotes a healthy lifestyle and supports cognitive function.
Fats and Cognitive Development
The impact of fats on cognitive development is significant. Studies have shown a correlation between adequate intake of healthy fats, particularly omega-3s, and improved cognitive skills in children. These skills include attention span, memory, and problem-solving abilities. Sufficient intake of healthy fats can significantly contribute to improved learning and development outcomes.
Moreover, healthy fats are crucial for the development of the hippocampus, a brain region vital for learning and memory. A diet rich in healthy fats can contribute to better learning and memory.
Fats and Brain Health Throughout Life
The importance of fats extends beyond childhood. Maintaining a balanced diet rich in healthy fats is vital throughout life for optimal brain function and preventing age-related cognitive decline. A diet rich in healthy fats can help maintain cognitive function as we age. Regular consumption of foods rich in omega-3s and other essential fatty acids can support memory, focus, and overall mental well-being throughout adulthood.
Incorporating healthy fats into your diet is a proactive approach to supporting brain health and promoting cognitive function at any stage of life. Regular intake of foods with healthy fats may help to reduce the risk of age-related cognitive decline.
Migraine isn't a one-size-fits-all condition. The intensity, duration, and even the specific symptoms can vary dramatically from person to person. Some individuals experience debilitating throbbing pain on one side of the head, accompanied by nausea and sensitivity to light and sound. Others might encounter a dull, persistent ache that spreads throughout their head. This diverse range of presentations highlights the importance of understanding individual experiences and tailoring treatment approaches accordingly, recognizing that what works for one person might not work for another.

Vitamins and Minerals: Essential for Overall Health
Vitamins for Growth and Development
Vitamins play a crucial role in various bodily functions, particularly during periods of rapid growth, like in puppies. Essential vitamins like Vitamin A are vital for healthy vision, immune function, and cell growth. Adequate Vitamin A intake supports the development of strong bones and tissues, ensuring a healthy skeletal structure crucial for playful puppies. Furthermore, Vitamin C contributes significantly to collagen production, which is vital for healthy skin, joints, and blood vessels. A balanced diet rich in Vitamin C is essential for a puppy's overall well-being, supporting their immune system and aiding in wound healing.
Vitamin D is another key player in bone health. It aids in calcium absorption, a process essential for strong teeth and bones. Sunlight exposure is a great source of Vitamin D, but a balanced diet incorporating foods rich in Vitamin D is also important for ensuring adequate intake. Furthermore, Vitamin E acts as a powerful antioxidant, protecting cells from damage and supporting immune function. Providing a balanced diet rich in a variety of foods is crucial to ensure your puppy receives all the necessary vitamins for optimal growth and development.
Minerals for Strong Bones and Muscles
Minerals are equally important for the development of strong bones, muscles, and overall health in puppies. Calcium is a cornerstone mineral, essential for bone formation. Adequate calcium intake is crucial during the crucial growth phase of a puppy's life. A diet deficient in calcium can lead to skeletal problems and weakened bones, which can affect a puppy's mobility and overall quality of life. Providing a diet rich in calcium-rich foods, such as dairy products (if appropriate for your puppy) or specific puppy food formulas, is a vital part of ensuring optimal bone health.
Phosphorus is another crucial mineral that works alongside calcium in building strong bones. It's essential for various bodily functions, including energy production and cell growth. A balanced ratio of calcium and phosphorus is essential for healthy bone development, and a diet insufficient in phosphorus can hinder this process. Iron is also essential for proper red blood cell production. Iron deficiency can lead to anemia, which can cause lethargy, weakness, and poor growth in puppies. A diet rich in iron-rich foods is vital for preventing such issues. Furthermore, zinc plays a critical role in immune function and wound healing, supporting a healthy immune response in growing puppies.
Other essential minerals like magnesium and potassium contribute to various bodily functions, including muscle function and nerve transmission. Ensuring your puppy receives a balanced intake of these minerals through a nutritious diet is crucial for their overall health and development. Consult with a veterinarian to determine the specific mineral needs of your puppy based on their breed, age, and activity level.
Read more about Nutritional Needs of Growing Puppies
Hot Recommendations
- Best Pet Bowls: Stainless Steel and Ceramic
- Pet Hydration: Why It's Crucial
- Stop Counter Surfing: Training Your Dog to Stay Off
- Pet Hypothyroidism: Symptoms and Management
- Signs of Pet Liver Disease: What to Watch For
- Pet Emergency Kits: What to Pack
- Dangers of Xylitol: Toxic to Dogs
- Dealing with Pet Diarrhea: When to See a Vet
- Preparing Pets for Travel: Tips for a Smooth Trip
- Pet Depression: Recognizing the Signs