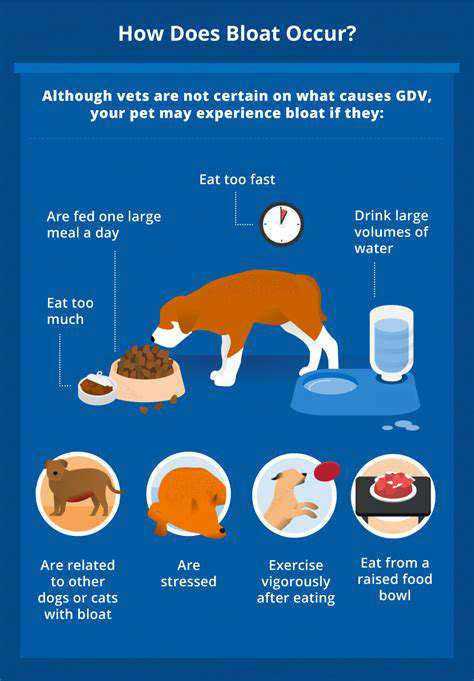
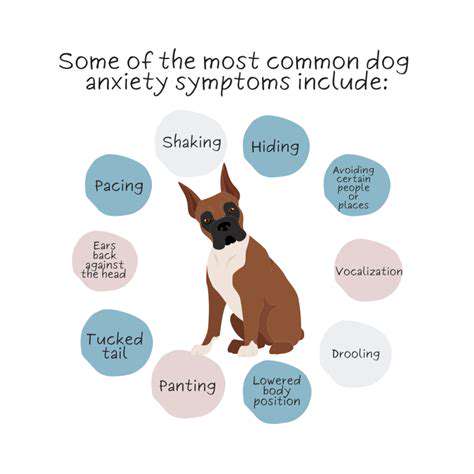
Grain Free vs. Grain Inclusive Pet Foods: The Latest Debate
The Nutritional Debate Surrounding Grain-Free Diets
The grain-free diet, a dietary approach that excludes grains like wheat, barley, and rye, has gained significant popularity in recent years, often touted as a solution for various health issues. Advocates often claim these diets can alleviate symptoms of conditions like irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) and celiac disease, while others suggest it can improve overall well-being and weight management. However, the scientific evidence supporting these claims remains somewhat inconclusive and often contested by medical professionals.
Many people adopt grain-free diets based on anecdotal evidence or perceived improvements in symptoms. However, rigorously controlled studies are often lacking to confirm these observations. This lack of robust scientific data makes it difficult to definitively determine the effectiveness of grain-free diets for specific conditions or general health improvements. Furthermore, a diet that excludes an entire food group like grains could potentially lead to nutritional deficiencies if not carefully planned and monitored by a healthcare professional.
It's crucial to understand that the human body requires a diverse range of nutrients to function optimally. Excluding an entire food group, like grains, without a clear understanding of individual needs and without proper substitutions, could lead to deficiencies in essential vitamins, minerals, and fiber, which are often abundant in grains. A well-balanced diet, focusing on whole foods and diverse nutrient sources, is generally recommended for overall health and well-being.
Potential Benefits and Drawbacks of Eliminating Grains
While the scientific evidence remains inconclusive, some potential benefits of excluding grains are often cited. For example, some individuals report experiencing reduced digestive discomfort or improved energy levels after eliminating grains from their diet. This could be particularly relevant for people with conditions like celiac disease or non-celiac gluten sensitivity.
However, the potential drawbacks of a grain-free diet can be substantial, especially if not carefully planned and monitored. Grains are a significant source of complex carbohydrates, fiber, and essential nutrients. Replacing them entirely with other food groups requires a comprehensive understanding of nutritional needs and suitable substitutions, which may not always be readily apparent.
Furthermore, the grain-free diet can sometimes be quite restrictive and potentially lead to social challenges. Many traditional meals and social gatherings revolve around foods containing grains. This could make it difficult to maintain this dietary approach in everyday life. It's essential to carefully consider the potential trade-offs between perceived benefits and potential drawbacks before embarking on any restrictive dietary plan.
A balanced and well-informed approach, with guidance from a healthcare professional or registered dietitian, is crucial for optimizing health and ensuring that a grain-free diet is sustainable and does not lead to deficiencies.
The Importance of a Balanced Diet and Ingredient Quality

Fueling Your Body for Optimal Health
A balanced diet is crucial for maintaining overall well-being and supporting a healthy lifestyle. It provides your body with the essential nutrients it needs to function optimally, from building and repairing tissues to supporting your immune system. A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins provides the building blocks for a strong and resilient body. This approach also contributes to a healthy weight management and reduces the risk of chronic diseases.
The importance of a balanced diet extends beyond physical health. It directly impacts your energy levels, mood, and cognitive function. The right nutrients can help you feel more focused and alert throughout the day. A balanced diet can also improve your sleep quality, leading to greater overall well-being and productivity.
The Role of Macronutrients in Diet
Macronutrients, including carbohydrates, proteins, and fats, are essential components of a balanced diet. Carbohydrates provide energy, proteins are vital for building and repairing tissues, and fats are crucial for hormone production and nutrient absorption. Understanding the appropriate proportions of each macronutrient is key to optimizing your diet. Each plays a vital role in maintaining overall health.
A balanced intake of carbohydrates, proteins, and fats is essential for optimal bodily functions. Consuming adequate carbohydrates ensures your body has a consistent source of energy. Protein is necessary for tissue growth and repair, while healthy fats are important for hormone production and nutrient absorption.
Micronutrients and Their Significance
Micronutrients, including vitamins and minerals, are essential for various bodily functions, although they are needed in smaller quantities than macronutrients. These micronutrients play a critical role in supporting metabolism, immune function, and cell growth. A deficiency in even one micronutrient can negatively impact overall health.
Vitamins and minerals are the unsung heroes of a healthy diet. Each vitamin and mineral plays a specific role in supporting crucial bodily functions. For instance, Vitamin C supports the immune system, while Iron is crucial for oxygen transport. By ensuring you consume a wide variety of nutrient-rich foods, you'll be providing your body with the vital micronutrients it needs to thrive.
The Impact of a Balanced Diet on Well-being
A balanced diet isn't just about physical health; it significantly impacts mental well-being too. Proper nutrition can boost mood, reduce stress, and enhance cognitive function. Choosing whole, unprocessed foods over highly processed options is a key part of a balanced diet. The benefits of a balanced diet extend to improved energy levels, better sleep quality, and a stronger immune system.
A well-nourished body is a healthier body, and a healthy body is a happier body. Eating a balanced diet can positively influence your mental well-being, contributing to a more positive outlook and reduced stress levels. This holistic approach to nutrition fosters a sense of overall well-being and can significantly improve your quality of life.
Read more about Grain Free vs. Grain Inclusive Pet Foods: The Latest Debate
Hot Recommendations
- Best Pet Bowls: Stainless Steel and Ceramic
- Pet Hydration: Why It's Crucial
- Stop Counter Surfing: Training Your Dog to Stay Off
- Pet Hypothyroidism: Symptoms and Management
- Signs of Pet Liver Disease: What to Watch For
- Pet Emergency Kits: What to Pack
- Dangers of Xylitol: Toxic to Dogs
- Dealing with Pet Diarrhea: When to See a Vet
- Preparing Pets for Travel: Tips for a Smooth Trip
- Pet Depression: Recognizing the Signs