Territorial Aggression in Dogs: Understanding and Managing
Recognizing the Signs of Territorial Aggression
The progression from alert to aggressive behavior typically follows a recognizable pattern. Early signs include:1. Increased alertness (perked ears, focused stare)2. Low growling or talkative barking3. Body stiffening and raised hackles4. Lunging or charging behaviorsThe critical window for intervention comes before stage 4, when the dog is still capable of being redirected. Waiting until biting occurs means the situation has escalated dangerously.
Managing Territorial Behaviors through Training
Effective training combines three key elements:1. Desensitization - Gradually exposing the dog to triggers at manageable intensities2. Counterconditioning - Creating positive associations with previously scary stimuli3. Alternative behaviors - Teaching incompatible actions (like go to mat) instead of barkingFor example, when working on door reactivity:- Start with recordings of doorbell sounds at very low volume- Reward calm behavior with high-value treats- Gradually increase volume over multiple sessions- Eventually practice with actual visitors
Seeking Professional Guidance for Persistent Issues
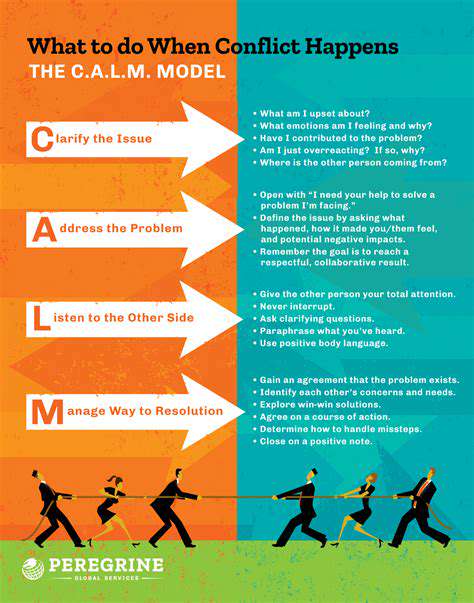
When home efforts plateau, consulting a certified behaviorist can provide breakthrough insights. These professionals assess:- The dog's complete behavioral history- Precise trigger thresholds- Family dynamics affecting the behavior- Underlying medical contributorsThey can then design a customized behavior modification plan with measurable milestones.

Environmental Modifications for a Secure Space
Minimizing Environmental Triggers
Strategic environmental adjustments can reduce territorial responses by up to 60% according to recent studies. Start by identifying hot spots where reactions most often occur - these are typically entry points (doors, gates) or resource areas (food bowls, favorite resting spots).
Simple changes like:- Rearranging furniture to reduce sightlines to triggers- Using frosted window film to obscure outside movement- Creating physical barriers with baby gatescan make dramatic differences in a dog's stress levels.
Strategic Space Allocation
Dogs benefit enormously from having clearly defined zones for different activities. The ideal home setup includes:- A safe haven retreat area (often a crate or bed in a quiet corner)- Designated play and feeding areas- Clear pathways between zonesThe most successful arrangements allow the dog to observe household activity without feeling compelled to guard every space.
Noise Reduction and Soundproofing
For sound-sensitive dogs, consider:- White noise machines to mask outside sounds- Heavy curtains to absorb noise- Door sweeps to reduce hallway echoes- Pressure-mounted window insertsThese modifications are particularly helpful for apartment dogs reacting to hallway noises.
Controlling Access and Circulation
Implementing structured access protocols helps dogs understand:- Which areas are always off-limits- Where they're welcome at specific times- How to move through the house appropriatelyUsing visual cues like different colored rugs or baby gates creates clear boundaries dogs readily understand.
Professional Guidance and Seeking Support
Understanding the Roots of Aggression
Territorial responses exist on a spectrum from normal to pathological. The critical distinction lies in the dog's ability to recover and accept redirection. Dogs that remain hypervigilant for extended periods or whose reactions intensify over time typically need professional intervention.
Effective Communication and Training
Modern training emphasizes:- Reward-based methods (treats, praise, play)- Clear, consistent signals- Manageable training sessions (5-10 minutes)- Gradual difficulty progressionAvoid common pitfalls like:- Inadvertently rewarding the unwanted behavior- Inconsistent enforcement of rules- Moving too quickly through training steps
Seeking Professional Veterinary and Behavioral Guidance
A comprehensive evaluation should assess:1. Medical factors (pain, neurological issues, hormonal imbalances)2. Learning history (previous training, traumatic experiences)3. Current environment (home setup, family routine)4. Genetic predispositions (breed tendencies)The most effective plans address all four areas simultaneously rather than focusing solely on behavior modification.
Long-Term Management and Prevention
Successful long-term strategies incorporate:- Regular refresher training sessions- Ongoing environmental adjustments as needs change- Careful monitoring of new potential triggers- Family-wide consistency in handling proceduresRemember that territorial tendencies may fluctuate with age, health status, and household changes - staying observant allows for timely adjustments.