Stop Dog Jumping: Training Your Pup to Greet Politely
Identifying the Triggers: When Does the Jumping Happen?
Understanding the Motivation
Dogs jump for a variety of reasons, often stemming from a combination of learned behaviors and instinctual responses. Understanding the underlying motivations behind the jumping is crucial to effectively addressing the issue. For example, a dog might jump to greet you enthusiastically, seeing you as a source of excitement and attention. This behavior, while endearing, can become problematic if not managed properly. It's important to consider the dog's past experiences and how they've learned to associate certain situations with rewards.
Sometimes, a dog jumps out of a need for attention. They might have learned that jumping gets them what they want, whether it's a treat, a game, or simply a reaction from you. Identifying these underlying motivations helps tailor a more effective training approach.
Identifying the Timing of the Jumps
Pay close attention to when your dog jumps. Is it when you arrive home? When you pick up their leash? Or when you're interacting with other people or animals? Pinpointing the specific triggers helps you understand the context and develop targeted solutions.
Keeping a log or journal can be helpful. Note down the time, the location, and any other relevant details, such as who or what was present. This detailed record can provide valuable insights into the triggers and help you create a more effective training plan.
Environmental Factors
The environment plays a significant role in triggering jumping behavior. A dog might jump more frequently in certain locations, such as at the entrance to the house, or when encountering specific sights or sounds. Understanding these environmental cues can help prevent jumping episodes.
Social Interactions and Other Dogs
Social interactions can significantly influence a dog's jumping behavior. A dog might jump more enthusiastically when meeting other dogs or people, particularly if they are strangers. This often stems from a dog's need to assert themselves, or to engage with others.
Your Body Language and Reactions
Your own body language and reactions can inadvertently reinforce jumping behavior. If you react excitedly when your dog jumps, even if it's an attempt to stop the behavior, you are inadvertently rewarding the jumping. Understanding your reactions and adjusting your body language are key components of an effective training strategy.
Reinforcing Desired Behaviors
Instead of focusing solely on stopping the jumping, consider rewarding alternative behaviors. For example, teach your dog to sit or lie down when guests arrive. By rewarding these desired behaviors, you can help your dog learn that these actions are more likely to result in positive outcomes. This positive reinforcement approach focuses on what you *want* your dog to do, rather than simply punishing unwanted behavior.
Positive Reinforcement: The Key to Success

Understanding Positive Reinforcement
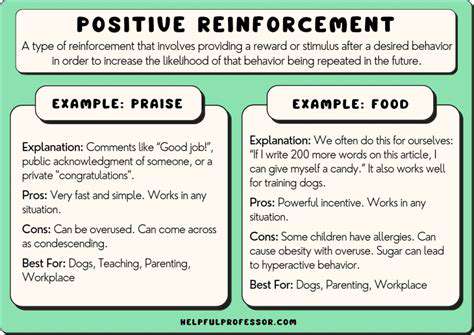
Positive reinforcement is a fundamental concept in behavior modification and learning. It involves adding a desirable stimulus after a behavior to increase the likelihood of that behavior occurring again in the future. This can be anything from a simple verbal praise to a tangible reward, and its effectiveness lies in associating the desired behavior with a positive consequence. Understanding this association is crucial for shaping desired responses.
Positive reinforcement is a powerful tool for both personal and professional development. It fosters a positive learning environment and encourages individuals to strive for improvement. By consistently rewarding desired actions, we can motivate ourselves and others to achieve more.
Types of Positive Reinforcement
Positive reinforcement can take many forms. Tangible rewards, such as stickers, treats, or small toys, are often effective for younger children. Verbal praise, such as good job or well done, can be incredibly motivating for people of all ages. Social recognition, like a pat on the back or a high five, can also be highly effective in reinforcing desired behaviors. Ultimately, the most effective type of positive reinforcement depends on the individual and the specific situation.
Choosing the right type of reinforcement is crucial for maximizing its impact. A child might be motivated by a sticker, while an adult might respond better to a compliment or an opportunity for advancement.
Applying Positive Reinforcement Effectively
To maximize the effectiveness of positive reinforcement, it's crucial to be consistent and timely in your delivery. The reward should be given immediately after the desired behavior occurs, making the connection between the action and the consequence clear. This immediacy strengthens the association and reinforces the behavior more effectively.
Consistency is key. If the reward isn't consistently delivered, the association between the behavior and the positive consequence weakens, potentially diminishing the effectiveness of the reinforcement strategy.
Examples of Positive Reinforcement in Action
Positive reinforcement can be applied in numerous settings. In the classroom, a teacher might reward students who complete their assignments on time with extra recess time or praise. At home, parents might reward children for tidying their rooms with extra screen time or a special treat. In the workplace, managers might reward employees for exceeding targets with bonuses or promotions.
These examples demonstrate the versatility of positive reinforcement. It's not limited to a specific context; it can be used in virtually any situation to encourage desired behaviors.
The Importance of Positive Reinforcement
Positive reinforcement plays a significant role in fostering positive relationships and creating a supportive environment. By focusing on what people are doing well, rather than dwelling on shortcomings, we create an atmosphere of encouragement and growth. This approach cultivates a healthy sense of self-worth and motivation. Furthermore, positive reinforcement techniques can be particularly beneficial in addressing challenging behaviors, offering a more constructive and effective alternative to punishment.
It encourages a growth mindset and promotes a more positive outlook on learning and development, regardless of age or circumstance.
Potential Pitfalls of Using Positive Reinforcement
While generally effective, positive reinforcement isn't without its potential drawbacks. Overusing rewards can sometimes lead to dependence on external validation, reducing intrinsic motivation. Also, rewards need to be carefully chosen to avoid creating unintended consequences, such as fostering competition or resentment among individuals. Careful consideration is needed to ensure that the rewards are appropriate and do not undermine the intrinsic value of the desired behavior.
Careful consideration and implementation are essential to avoid potential pitfalls and maximize the benefits of positive reinforcement.
Redirecting Energy and Attention: A Multi-pronged Approach
Understanding the Root Cause of Jumping
Dog jumping, a common behavioral issue, is often rooted in a combination of factors. It could be a learned behavior reinforced by attention, whether positive or negative. A dog might jump for excitement, anticipation of play, or even as a way to assert dominance, particularly if they feel they aren't getting enough attention or have a lack of clear boundaries. Understanding the specific triggers behind your dog's jumping is crucial for effective training.
Recognizing these underlying motivations will help you tailor your training approach and avoid inadvertently reinforcing the behavior through your responses. The jumping behavior itself can be a complex response to various stimuli, making it critical to identify the specific triggers and motivations before implementing any training strategies.
Establishing Clear Boundaries and Rules
Consistency is key to establishing clear boundaries. A dog needs to understand what is acceptable and unacceptable behavior. This involves creating clear rules around greetings and interactions. For example, designating a specific greeting zone or area where jumping is not tolerated, and consistently enforcing these rules. This consistent response reinforces the desired behavior and helps the dog understand the expectations.
Using clear body language and verbal cues can also help communicate these boundaries effectively. Avoid interacting with your dog when they're jumping, and redirect them to a more appropriate behavior, like sitting or staying. This method helps to teach the dog that jumping doesn't lead to the desired interaction or reward.
Redirecting Attention and Energy
A significant aspect of addressing dog jumping involves redirecting your dog's attention and energy. This often involves providing alternative activities that engage your dog mentally and physically. Engaging in interactive games, puzzle toys, or training sessions can help channel their energy in a positive direction.
Providing ample opportunities for exercise and mental stimulation can significantly reduce the likelihood of jumping. A tired dog is less likely to exhibit unwanted behaviors like jumping, making regular walks and playtime essential components of a comprehensive training strategy. Consider incorporating activities that encourage focus and obedience.
Positive Reinforcement Techniques
Positive reinforcement techniques form the foundation of effective dog training. When your dog exhibits calm and appropriate greetings, reward that behavior immediately with praise, treats, or toys. This positive reinforcement strengthens the desired response and helps the dog associate calm greetings with positive outcomes. Rewarding calm behavior not only encourages the desired behavior, but also creates a more positive and enjoyable experience for both you and your dog.
Ignoring the Jumping Behavior
Ignoring the jumping behavior is a powerful tool, but it must be done strategically. Resist the urge to interact with your dog when they're jumping. This means avoiding eye contact, verbal responses, or physical interactions. The key here is to avoid giving the dog any attention while they're jumping.
Desensitization and Counter-Conditioning
Desensitization and counter-conditioning are advanced techniques that gradually expose your dog to the stimuli that trigger jumping, while pairing these stimuli with a more desirable response. This involves gradually introducing the triggers, starting with minimal exposure and increasing it as your dog becomes more comfortable. This process helps the dog to associate the triggers with positive experiences rather than the jumping response.
Consistency and Patience
Ultimately, consistent application of the outlined strategies, coupled with patience, is essential for success. Training takes time and effort. Celebrate small victories and remain consistent in your approach, reinforcing the desired behaviors and providing clear boundaries. Remember that every dog learns at a different pace, so be patient and understanding throughout the process.

Read more about Stop Dog Jumping: Training Your Pup to Greet Politely
Hot Recommendations
- Best Pet Bowls: Stainless Steel and Ceramic
- Pet Hydration: Why It's Crucial
- Stop Counter Surfing: Training Your Dog to Stay Off
- Pet Hypothyroidism: Symptoms and Management
- Signs of Pet Liver Disease: What to Watch For
- Pet Emergency Kits: What to Pack
- Dangers of Xylitol: Toxic to Dogs
- Dealing with Pet Diarrhea: When to See a Vet
- Preparing Pets for Travel: Tips for a Smooth Trip
- Pet Depression: Recognizing the Signs