Pet Cushing's Disease: Symptoms and Treatment
Diagnostic Procedures for Cushing's Disease
Initial Assessment and History Taking
A crucial first step in diagnosing Cushing's syndrome is a thorough patient history. This involves carefully questioning the patient about potential symptoms, such as unexplained weight gain, particularly in the face and upper back, thinning of the skin, easy bruising, and changes in mood or behavior. Collecting information about recent medication use, including corticosteroids, is essential as these can be a primary cause of the condition. The timeline of symptom onset and progression can also provide valuable clues for diagnosis.
A detailed medical history, including a review of systems, is paramount for identifying potential risk factors and related conditions. This detailed history-taking process allows healthcare professionals to narrow down the possible causes and prioritize further diagnostic tests. Early recognition of Cushing's syndrome is critical for timely intervention and improved patient outcomes.
Physical Examination
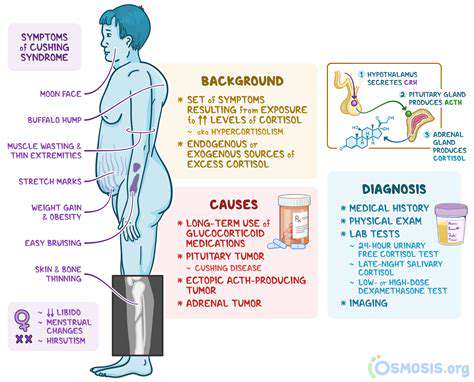
A comprehensive physical examination is essential to identify physical manifestations of Cushing's syndrome. This includes an assessment of body habitus, with particular attention to central obesity, moon face, buffalo hump, and striae. Evaluating skin integrity, checking for easy bruising, and noting any signs of hirsutism or muscle weakness are vital components of the physical exam. Blood pressure, pulse, and other vital signs should also be meticulously recorded.
Careful observation of physical characteristics, such as redistribution of fat and skin changes, is often the first indication of the condition. Physical examination results, combined with the patient's history, help clinicians formulate a preliminary diagnosis and guide the selection of further diagnostic tests.
Laboratory Tests
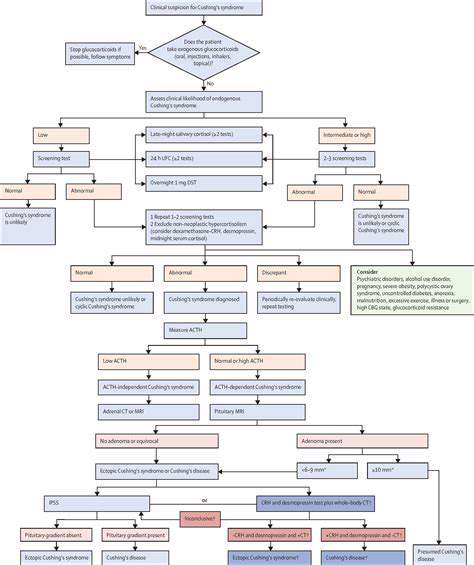
Several laboratory tests are commonly employed to aid in the diagnosis of Cushing's syndrome. These include a 24-hour urine cortisol test, which measures the levels of cortisol excreted in the urine over a 24-hour period. This test is particularly useful because it provides a comprehensive assessment of cortisol production over time. Plasma cortisol levels measured at various times during the day can also be helpful. Measuring plasma ACTH levels is also critical in differentiating between ACTH-dependent and ACTH-independent Cushing's.
Imaging Studies
Imaging studies, such as CT or MRI scans of the adrenal glands and pituitary gland, are often employed to identify potential abnormalities in these organs. These scans can help pinpoint the location of any tumors or other structural changes that might be contributing to Cushing's syndrome. CT scans provide detailed cross-sectional images of the body, while MRI scans offer superior soft-tissue contrast, allowing for a clearer visualization of the pituitary and adrenal glands. These images can reveal the presence or absence of tumors or other abnormalities that may be causing the hormonal imbalances.
Dexamethasone Suppression Test
The dexamethasone suppression test is a valuable diagnostic tool for assessing the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis. This test involves administering dexamethasone, a synthetic glucocorticoid, and measuring cortisol levels before and after administration. An abnormal response to dexamethasone can suggest the presence of Cushing's syndrome. This test helps distinguish between Cushing's syndrome and other conditions that may cause similar symptoms. The results of this test, along with other findings, help guide further investigations to confirm the diagnosis.
Differential Diagnosis
It is crucial to rule out other conditions that may present with symptoms similar to Cushing's syndrome. These conditions include obesity, stress, and certain medications. A differential diagnosis involves considering other possible causes and systematically eliminating them. This process is essential to ensure an accurate diagnosis and avoid unnecessary or inappropriate treatments. Careful evaluation of the patient's history, physical examination findings, and laboratory results, in addition to imaging studies, helps clinicians distinguish Cushing's syndrome from other conditions with overlapping symptoms.
Read more about Pet Cushing's Disease: Symptoms and Treatment
Hot Recommendations
- Best Pet Bowls: Stainless Steel and Ceramic
- Pet Hydration: Why It's Crucial
- Stop Counter Surfing: Training Your Dog to Stay Off
- Pet Hypothyroidism: Symptoms and Management
- Signs of Pet Liver Disease: What to Watch For
- Pet Emergency Kits: What to Pack
- Dangers of Xylitol: Toxic to Dogs
- Dealing with Pet Diarrhea: When to See a Vet
- Preparing Pets for Travel: Tips for a Smooth Trip
- Pet Depression: Recognizing the Signs