Common Skin Conditions in Pets
Fungal Infections: Ringworm and Yeast Dermatitis
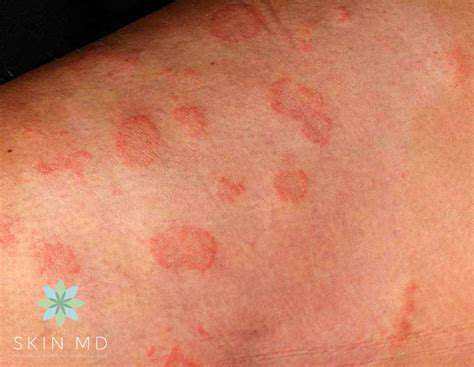
Ringworm: A Common Fungal Infection
Ringworm, despite its name, is not caused by worms but rather by a fungal infection affecting the skin, hair, and nails. This condition manifests as a distinctive circular rash with scaly edges. Contrary to popular belief, ringworm has nothing to do with actual worms - it's entirely fungal in nature. The infection spreads easily through direct contact with infected individuals or contaminated surfaces.
Understanding ringworm's true nature is the first step toward effective prevention and treatment. Early recognition of symptoms allows for quicker medical intervention, which can significantly reduce both the duration of infection and risk of spreading it to others. Proper hygiene practices become crucial when dealing with this highly contagious condition.
Yeast Infections: A Closer Look
Yeast infections, medically termed candidiasis, result from overgrowth of Candida albicans fungus. These infections can develop in various body areas including skin folds, the mouth, and genital regions. Symptoms typically involve noticeable redness, persistent itching, and sometimes a thick, white discharge.
Certain populations prove more susceptible to yeast infections, particularly those with weakened immune systems. Factors like prolonged antibiotic use, hormonal fluctuations, and chronic health conditions can create ideal conditions for yeast overgrowth. Maintaining proper hygiene and supporting immune health through diet and lifestyle choices plays a vital role in prevention.
Diagnosis and Treatment Approaches
Healthcare providers typically diagnose fungal infections through physical examination, though sometimes laboratory tests are necessary. Treatment usually involves antifungal medications in various forms - creams for topical application or oral medications for more severe cases. Completing the full course of treatment remains essential, even if symptoms improve, to prevent recurrence.
Prevention Strategies
Preventing fungal infections centers on moisture control and hygiene. Keeping skin dry, especially in body folds, significantly reduces infection risk. Avoiding shared personal items and laundering clothing/bedding regularly helps prevent spread. Supporting overall health through nutrition and exercise strengthens the body's natural defenses against fungal overgrowth.
Allergies: From Food to Environmental Triggers
Food Allergies: A Growing Concern
Food allergies represent an increasingly common health issue, especially among children. Reactions can range from mild discomfort to life-threatening anaphylaxis. Accurate identification of trigger foods and proper management strategies are essential for safety.
Environmental Allergies
Seasonal allergies (hay fever) result from reactions to airborne particles like pollen or dust mites. Symptoms often include sneezing, watery eyes, and nasal congestion. The severity varies considerably among individuals, with some experiencing minor irritation while others face significant quality-of-life impacts.
Genetic Factors
Allergy development has strong genetic components. Those with allergic parents face higher risks themselves. Ongoing research continues to uncover the complex interactions between genetics and environmental triggers.
Diagnosis and Management
Allergy testing helps identify specific triggers. Management combines avoidance strategies with medications like antihistamines. For severe cases, immunotherapy may help reduce sensitivity over time.
Parasites: Fleas, Ticks, and Mites
Fleas: Tiny Pests, Big Problems
Fleas are wingless insects that feed on animal blood, causing intense itching and skin irritation. Heavy infestations can lead to hair loss and secondary infections. Regular grooming and preventive treatments are key to control.
Ticks: Disease Vectors
These arachnids transmit serious illnesses like Lyme disease. Prompt removal and preventive measures are crucial, especially for outdoor pets.
Mites: Microscopic Troublemakers
Different mite species cause various conditions from ear infections to mange. Veterinary diagnosis ensures proper treatment.
Prevention and Treatment
Regular parasite prevention products, combined with veterinary care, provide the best protection. Early intervention prevents complications and more serious health issues.
Migraine represents a neurological condition involving severe, recurrent headaches often accompanied by nausea and light sensitivity. These episodes can significantly impact daily functioning.
Read more about Common Skin Conditions in Pets
Hot Recommendations
- Best Pet Bowls: Stainless Steel and Ceramic
- Pet Hydration: Why It's Crucial
- Stop Counter Surfing: Training Your Dog to Stay Off
- Pet Hypothyroidism: Symptoms and Management
- Signs of Pet Liver Disease: What to Watch For
- Pet Emergency Kits: What to Pack
- Dangers of Xylitol: Toxic to Dogs
- Dealing with Pet Diarrhea: When to See a Vet
- Preparing Pets for Travel: Tips for a Smooth Trip
- Pet Depression: Recognizing the Signs