Administering Pet Injections: A How To Guide
Choosing the Right Injection Technique
Understanding the Different Injection Techniques
Choosing the right injection technique for your pet is crucial for their comfort and safety. Different injection types are designed for various purposes and target specific tissues. Understanding these differences will enable you to select the appropriate method for administering medications, vaccinations, or other necessary treatments. This knowledge is essential for minimizing stress on your pet and ensuring accurate drug delivery, ultimately optimizing the treatment's effectiveness.
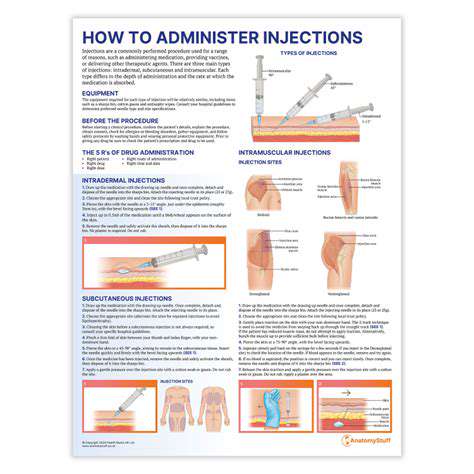
Intradermal injections, for example, are used for allergy testing and some vaccinations. Subcutaneous injections, on the other hand, are commonly used for administering insulin and other medications that need to be absorbed slowly into the bloodstream. Knowing the specific requirements of the injection will help you select the proper technique for maximum effectiveness and safety.
Preparing the Injection Site
Proper preparation of the injection site is paramount for minimizing discomfort and preventing infection. This involves carefully cleaning the area with a suitable antiseptic solution, ensuring thorough disinfection to remove any bacteria or contaminants. The selected antiseptic should be non-irritating to the pet's skin and should effectively eliminate pathogens to prevent potential complications from the procedure.
Gentle handling and restraint are essential throughout the process. A calm and reassuring approach will help to reduce your pet's anxiety and make the procedure as stress-free as possible. The goal is to create a comfortable and safe environment for both you and your pet.
Selecting the Appropriate Syringe and Needle
Selecting the correct syringe and needle size is critical for accurate and safe injection administration. The gauge and length of the needle should be tailored to the pet's size and the type of medication being administered. Using a needle that is too small may lead to difficulties in injection, while a needle that is too large can cause tissue damage and increase the risk of bleeding.
Consider the viscosity and volume of the medication when choosing the appropriate syringe. A syringe that is too small may make the injection difficult, while a syringe that is too large might introduce unnecessary volume into the body.
Administering the Injection
Once the injection site is prepared and the appropriate equipment is selected, the injection can be administered. Hold the syringe securely and insert the needle at the designated angle, ensuring the needle is inserted correctly into the target tissue. Administer the medication slowly and steadily to avoid injecting the medication too rapidly.
After administering the injection, gently remove the needle and apply gentle pressure to the injection site to stop any bleeding. Dispose of the used needle and syringe properly, following all safety guidelines.
Handling Potential Complications
While administering injections, be aware of potential complications. Reactions such as swelling, bruising, or infection at the injection site are possible. Knowing how to recognize these reactions and take appropriate action is crucial to ensure the well-being of your pet.
If any unusual reactions occur, contact your veterinarian immediately. They can provide guidance on how to manage the situation and determine the best course of action for your pet.
Post-Injection Care
Post-injection care involves monitoring your pet for any adverse reactions. This includes observing the injection site for signs of swelling, redness, or any other unusual changes. Keeping a close eye on your pet's overall behavior and vital signs is essential.
Following your veterinarian's instructions for post-injection care is critical for ensuring your pet's recovery and preventing potential complications. This might include providing pain relief, monitoring for any signs of infection, or recommending specific dietary changes.
Read more about Administering Pet Injections: A How To Guide
Hot Recommendations
- Best Pet Bowls: Stainless Steel and Ceramic
- Pet Hydration: Why It's Crucial
- Stop Counter Surfing: Training Your Dog to Stay Off
- Pet Hypothyroidism: Symptoms and Management
- Signs of Pet Liver Disease: What to Watch For
- Pet Emergency Kits: What to Pack
- Dangers of Xylitol: Toxic to Dogs
- Dealing with Pet Diarrhea: When to See a Vet
- Preparing Pets for Travel: Tips for a Smooth Trip
- Pet Depression: Recognizing the Signs